Backtracking - Quick Notes
- Fix section counts
- Add Word Break 2 - medium (though mentioned as hard)
- Palindrome partition + Word Break 2 - as one section
- Solve palindrome partition
- Other problems
- Matchstick
- Partition to K equal sum subset
- Letter combination
Every backtracking problem is essentially a DFS.
Backtracking has 4 pattern:
- T1 - Find a value
- Find the largest value (9)
- T2 - Find a set of values
- Find all of the distinct leaf node values [2 , 3, 1 , 1]
- T3 - Find the path
- Find the path with largest root to leaf sum [5, 9, 1]
- T4 - Find set of paths
- Find all the numbers represented by root lead paths
- [562, 563,591,591]
- Find all the numbers represented by root lead paths
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1vfKpbaYkpGFrjxYaswa3ZBG0GZ-w58v5/view?t=19
Subset, combination and permutations
Here's a clear and concise breakdown of subset, combination, and permutation in the context of an array:
🔹 Subset:
A subset is any selection of elements (including the empty set and full set), where order does not matter, and elements may be excluded.
-
2^n subsets
-
From array
[1, 2, 3]:-
Subsets:
[],[1],[2],[3],[1,2],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3] -
Total: 2n=23=82^n = 2^3 = 8 subsets
-
🔹 Combination:
A combination is a selection of k elements from the array, where order does not matter, and no repetition.
- From
[1, 2, 3], combinations of 2:
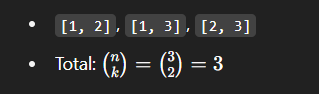
🔹 Permutation:
A permutation is an arrangement of k elements from the array, where order matters, and no repetition.
- From
[1, 2, 3], permutations of 2:

Summary Table
Combinations are subsets of size k where order does not matter.
| Term | Includes All Sizes? | Order Matters? | Repeats? | Example from [1,2,3] (k=2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subset (2^n) | Yes | No | No | [], [1], [2], [3], [1,2], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2,3]`. |
| Combination | No (fixed size k) | No | No | [1,2], [1,3], [2,3] |
| Permutation | No (fixed size k) | Yes | No | [1,2], [2,1], [1,3], [3,1] |
Notes
Neetcode 250 got 17 backtracking problems, out of these - 2 are not really backtracking!
-
Warm-ups - Subsets without duplicates elements - 2 questions:
-
Problems:
-
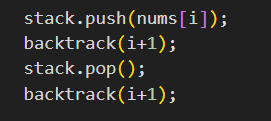
at every element - you have two choices - take it or leave it.
-
two kind of subsets - with or without element
-
-
Unique Subsets with duplicate elements - 1 question:
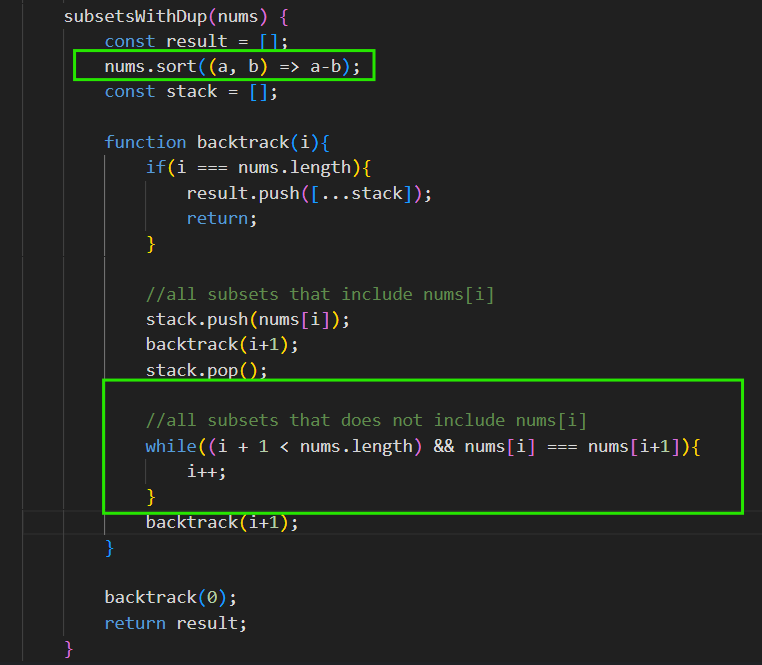
- Problems:
- Sort the array so that duplicates come next to each other
- Think why dups are coming
- subsets with elements are fine.
- but subsets which are not suppose to have the element get the element again due to duplicate elements and hence resulting into duplicate subset.
- so how to avoid it? Just bypass the next duplicate elements
-
Combination Target problems - 2 problems
- Key
- Usual array element branching will result into duplicate combinations.
- Take "diminishing" Target as your main entity for base conditions
- Problems:-
https://neetcode.io/problems/combination-target-sum
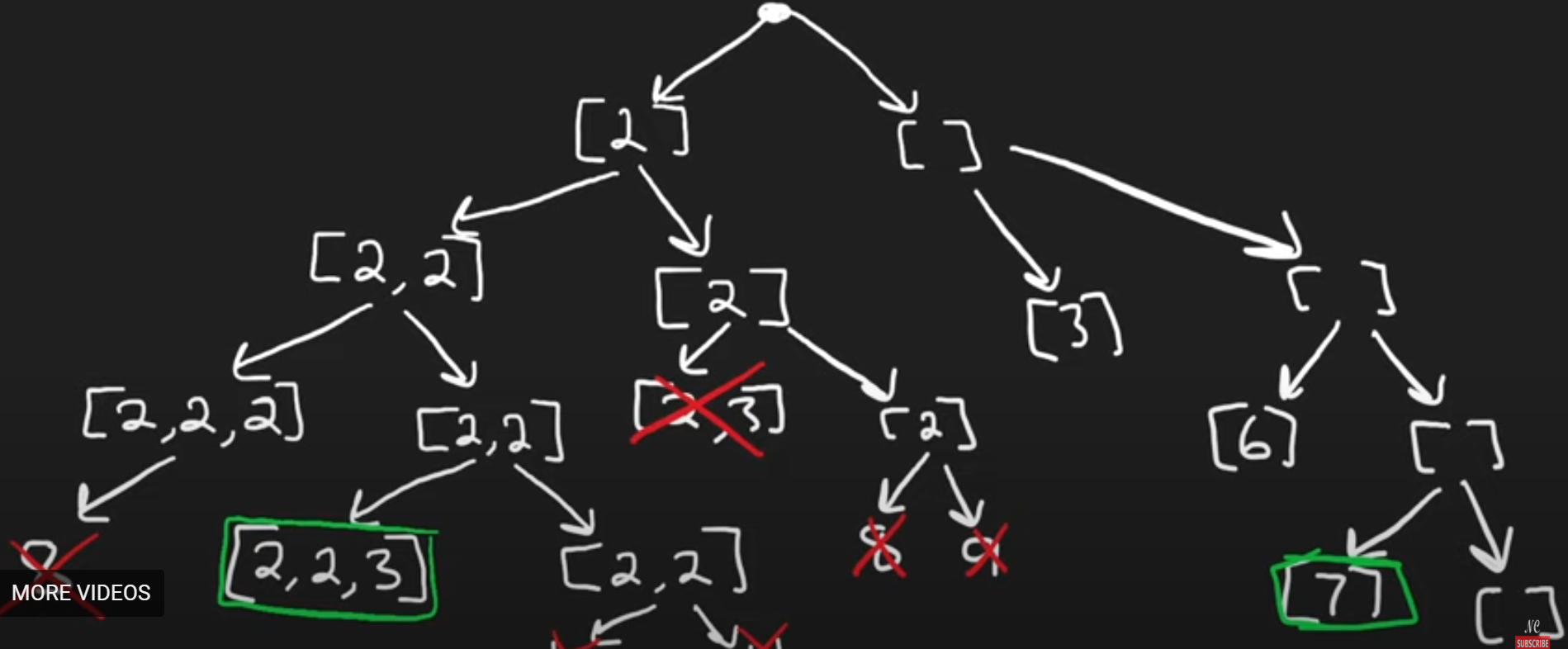
- This problem has unique tree because of condition "No duplicate combinations"
- Notice how we handled "The same number may be chosen from
numsan unlimited number of times." condition of problem by calling the dfs again with same index - Time and space: O(2^t) - t is target and height of tree

-
https://neetcode.io/problems/combination-target-sum-ii (Duplicate variation with "once" usage)
- Think why duplicates are coming and how to avoid? (same as subsets)
- Diff from above problem - Each number in
candidatesmay only be used once in the combination. 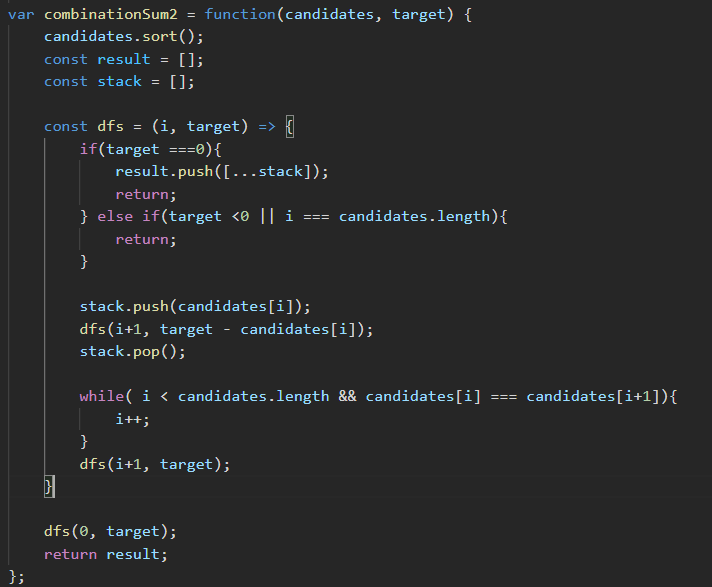
-
-
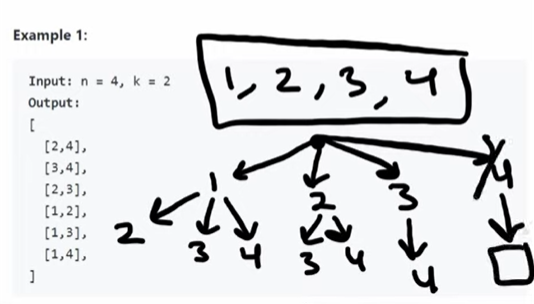
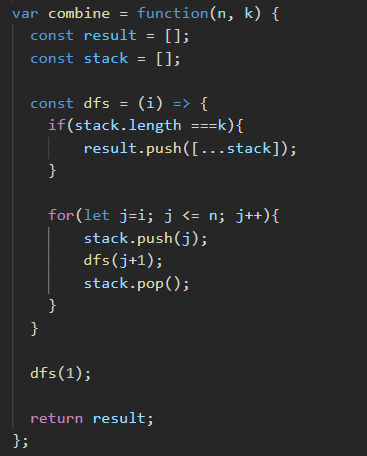
Combinations of Natural numbers - 1 problem
- Problems:
- https://neetcode.io/solutions/combinations
- Like duplicate probs above, here too we might end up with duplicate combinations, but here the trick to avoid dups is - to not go back to left/prev values. for 1, try with 2,3,4 - but for 2- try with 3,4 only
-
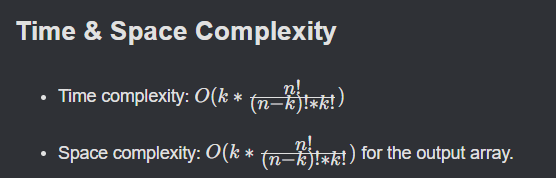
-
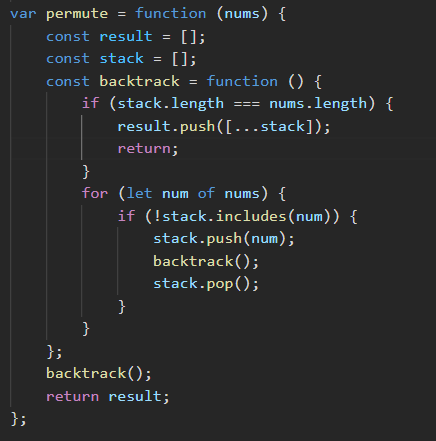
⭐Permutations of Array:
-
Problems:
-
https://neetcode.io/problems/permutations

-
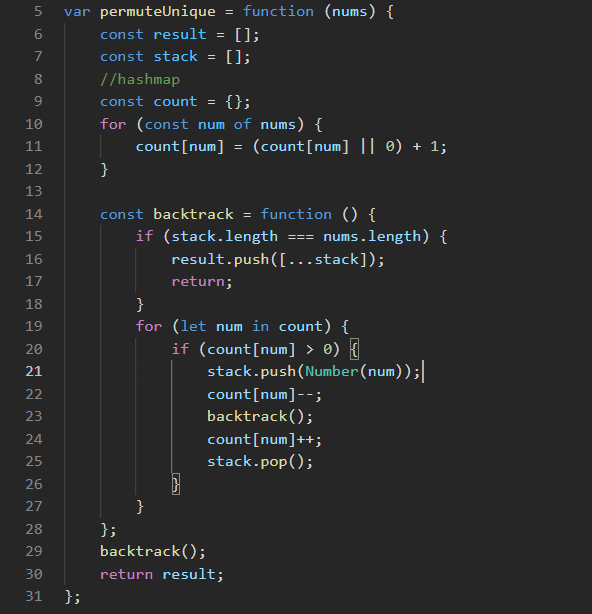
https://neetcode.io/solutions/permutations-ii (Duplicates)
- Convert the array into Hashmap with their freq.

Older solutions:
-
Remember the decision tree - Not exactly backtracking
- traditional backtracking tree (choose an option kinda) does not work here.

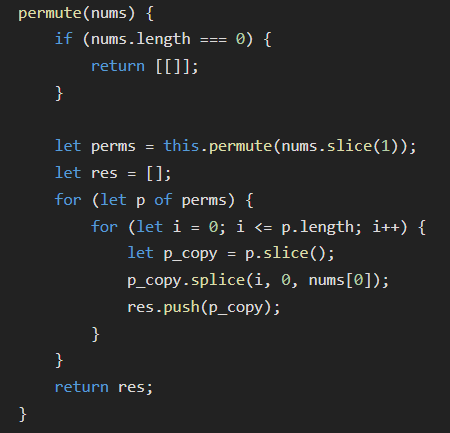
Runtime: O(n! * n^2)
Space: O(n! * n)Perm - II: Convert the array into Hashmap with their freq, and use
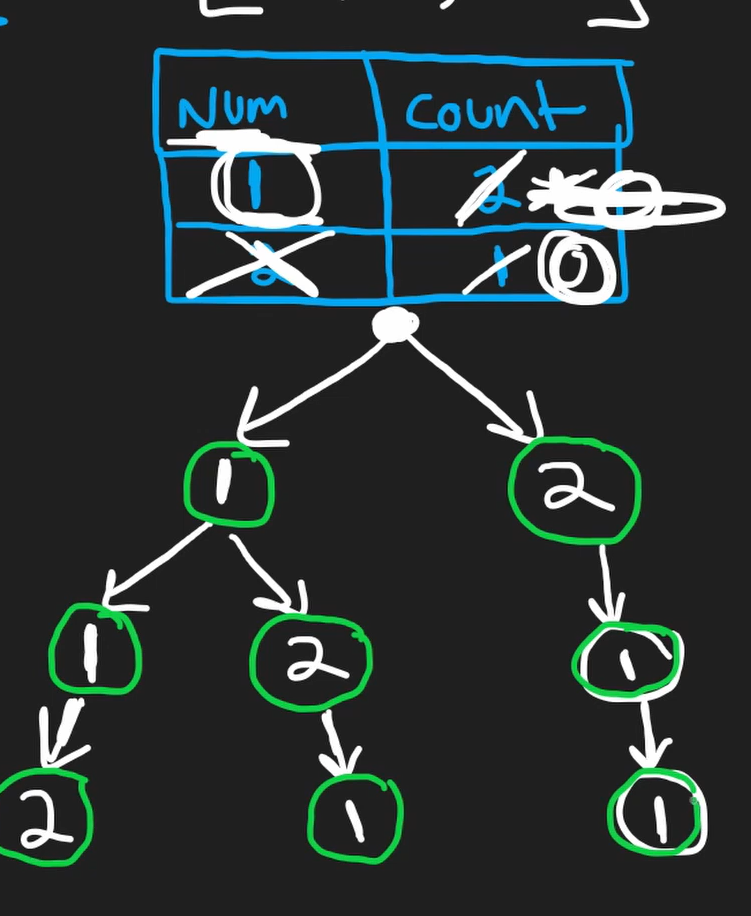
- traditional backtracking tree (choose an option kinda) does not work here.
-
-
-
Time complexity: O(n!∗n)O(n!∗n)
-
Space complexity: O(n!∗n)O(n!∗n) for the output list.
-
-
Word Search - Start a DFS from every cell
- Problem - https://neetcode.io/problems/search-for-word
- Start a DFS from every cell. Use Stack/path as Set because this time not only we want to keep track of journey - we also want "not to go to a seen node in current stack journey".
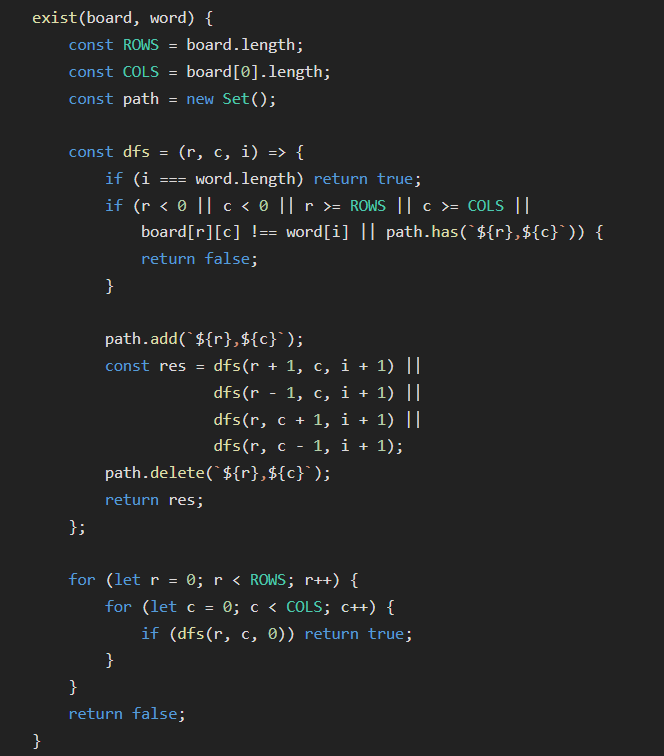
- Start a DFS from every cell. Use Stack/path as Set because this time not only we want to keep track of journey - we also want "not to go to a seen node in current stack journey".
- Problem - https://neetcode.io/problems/search-for-word
-
Palindrome Partitioning - https://neetcode.io/problems/palindrome-partitioning
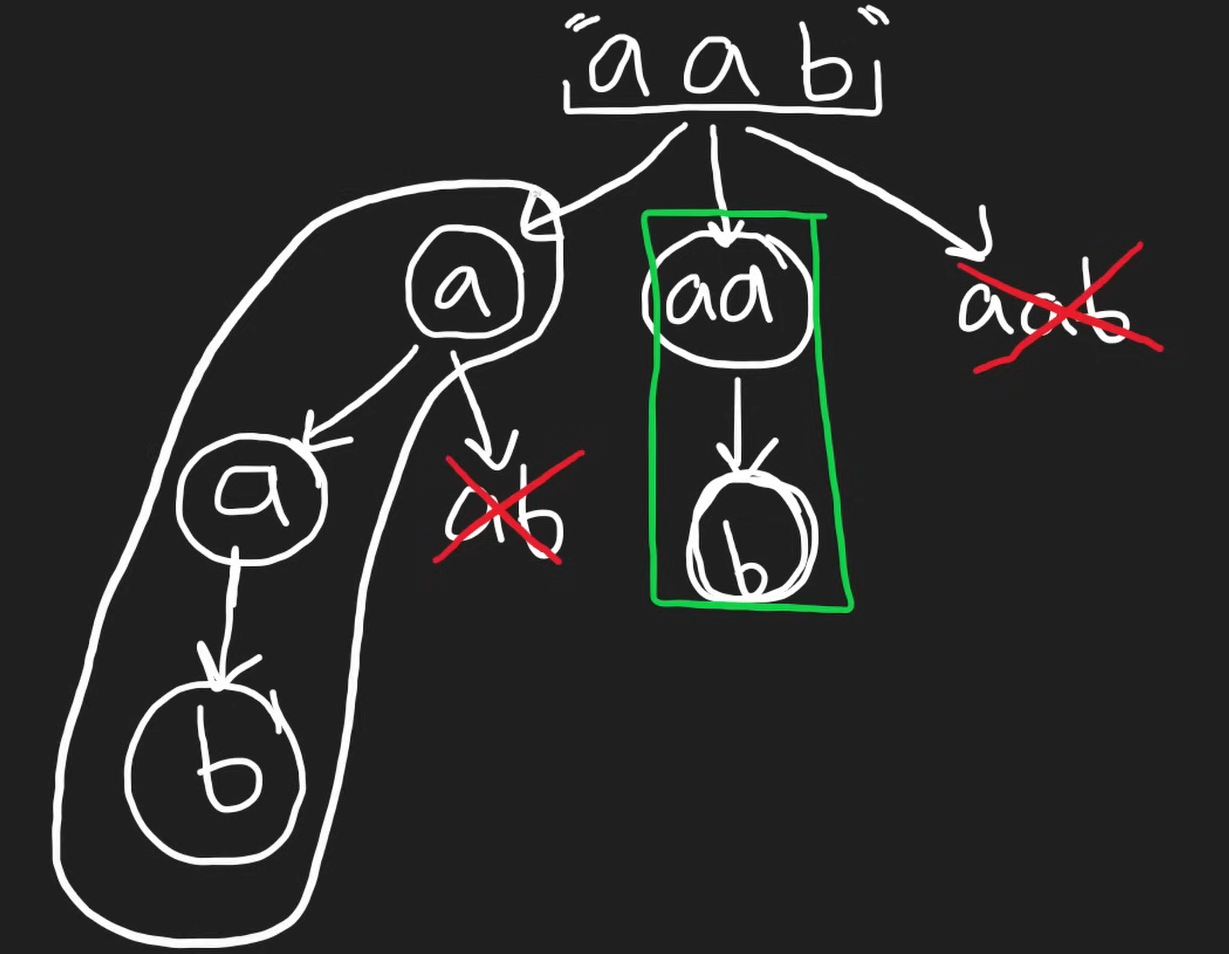
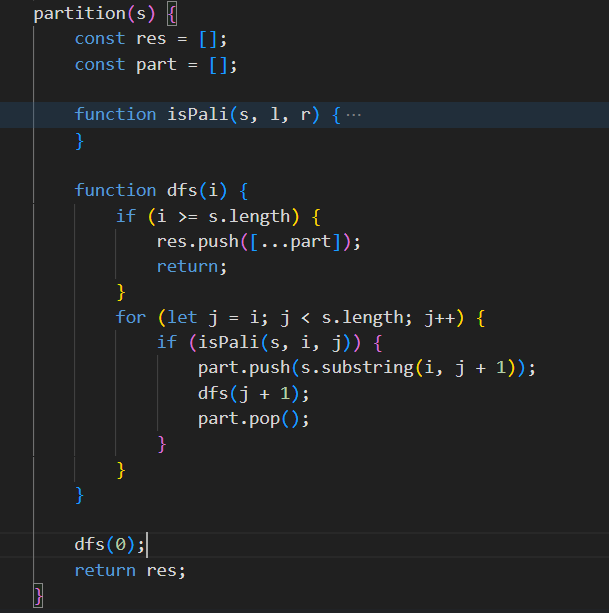
- N-Queens and N Queens II - 2 problems
- Problems
- https://neetcode.io/solutions/n-queens
- https://neetcode.io/solutions/n-queens-ii
- Just like 1st problem - just return the count of possibilities rather than possibilities
- No need of board/stack variable
- N Queens
- Three sets: columns, positive diagonals, negative diagonals
- Go row wise
- Time complexity: O(n!)
- Space complexity: O(n^2)
- Code highlights
- How they built initial array
- How they built output from board
- clean-up and backtracking
- base condition
- Problems
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {string[][]}
*/
solveNQueens(n) {
const col = new Set();
const posDiag = new Set();
const negDiag = new Set();
const res = [];
const board = Array.from({ length: n },
() => Array(n).fill('.'));
/**
* @param {number} r
* @return {void}
*/
function backtrack(r) {
if (r === n) {
res.push(board.map(row => row.join('')));
return;
}
for (let c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (col.has(c) || posDiag.has(r + c) ||
negDiag.has(r - c)) {
continue;
}
col.add(c);
posDiag.add(r + c);
negDiag.add(r - c);
board[r][c] = 'Q';
backtrack(r + 1);
col.delete(c);
posDiag.delete(r + c);
negDiag.delete(r - c);
board[r][c] = '.';
}
}
backtrack(0);
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
totalNQueens(n) {
const col = new Set();
const posDiag = new Set();
const negDiag = new Set();
let res = 0;
/**
* @param {number} r
* @return {void}
*/
function backtrack(r) {
if (r === n) {
res++;
return;
}
for (let c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (col.has(c) || posDiag.has(r + c) ||
negDiag.has(r - c)) {
continue;
}
col.add(c);
posDiag.add(r + c);
negDiag.add(r - c);
backtrack(r + 1);
col.delete(c);
posDiag.delete(r + c);
negDiag.delete(r - c);
}
}
backtrack(0);
return res;
}
}
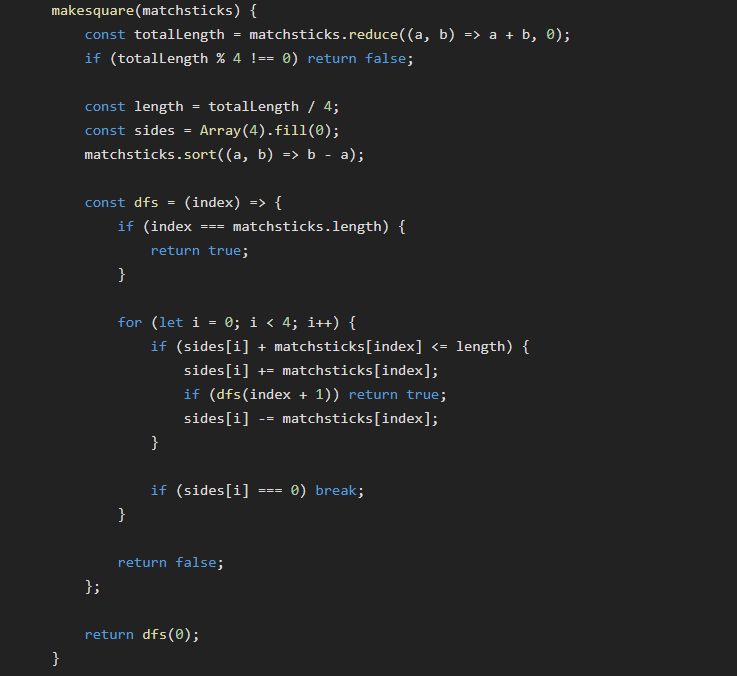
Matchsticks to square
- sum of all sticks should be divisible by 4 -> else false
- each side = sum(arr)/4
- any stick > side -> Can't use this stick hence false
- Reverse sorting input array can speed up code
- Now problem is a simple backtracking of index => backtrack(i)
- try keeping sticks in 4 sides (top, left, right, bottom)
- Backtrack - if current side length exceeds allowed stick
- Base - once you have finished arr.
- Time: o(4^n). Space: o(n)
Partition to K equal sum subset
- Time: o(k* 2^n), space: o(n)
- A bit unique problem where we build k backtracking trees of 2^n runtimes :|
- In order to identify what indexes are used in prev backtracking trees - we'll use additional array to mark what indexes are used.
- backtrack(i, k, subSetSum)
- Base: if k == 0 -> return true
- Base: if subSetSum == target -> start a new backtrack(0, k-1, 0)