Bit Operations
Here are concise notes on using bitwise operators in JavaScript — useful for interviews and coding practice:
🔹 Basics
JavaScript stores numbers as 64-bit floating point, but bitwise operators work on 32-bit signed integers.
-
Signed 32-bit integer → range:
-2,147,483,648to2,147,483,647 -
Bitwise ops truncate numbers to 32-bit, then back to JS Number.
🔹 Common Bitwise Operators
| Operator | Symbol | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| AND | & |
5 & 3 = 1 |
Bit is 1 only if both bits are 1 |
| OR | | |
5 | 3 = 7 |
Bit is 1 if at least one bit is 1 |
| XOR | ^ |
5 ^ 3 = 6 |
Bit is 1 if bits differ |
| NOT | ~ |
~5 = -6 |
Flips all bits (2’s complement) |
| Left Shift | << |
5 << 1 = 10 |
Shift left, fill with 0 |
| Right Shift (Sign-propagating) | >> |
5 >> 1 = 2 |
Shift right, keep sign bit |
| Unsigned Right Shift | >>> |
-5 >>> 1 = 2147483645 |
Shift right, fill with 0 |
🔹 Useful Tricks
- Check even/odd
let x = 7;
console.log(x & 1 ? "Odd" : "Even"); // Odd
- Swap two numbers without temp
let a = 5, b = 9;
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
console.log(a, b); // 9, 5
- Multiply or divide by 2
console.log(5 << 1); // 10 (5 * 2)
console.log(20 >> 2); // 5 (20 / 4)
- Check if k-th bit is set
let n = 13; // 1101
let k = 2; // (0-indexed from right)
console.log((n & (1 << k)) !== 0); // true (bit is set)
- Set a bit
n = n | (1 << k);
- Clear a bit
n = n & ~(1 << k);
- Toggle a bit
n = n ^ (1 << k);
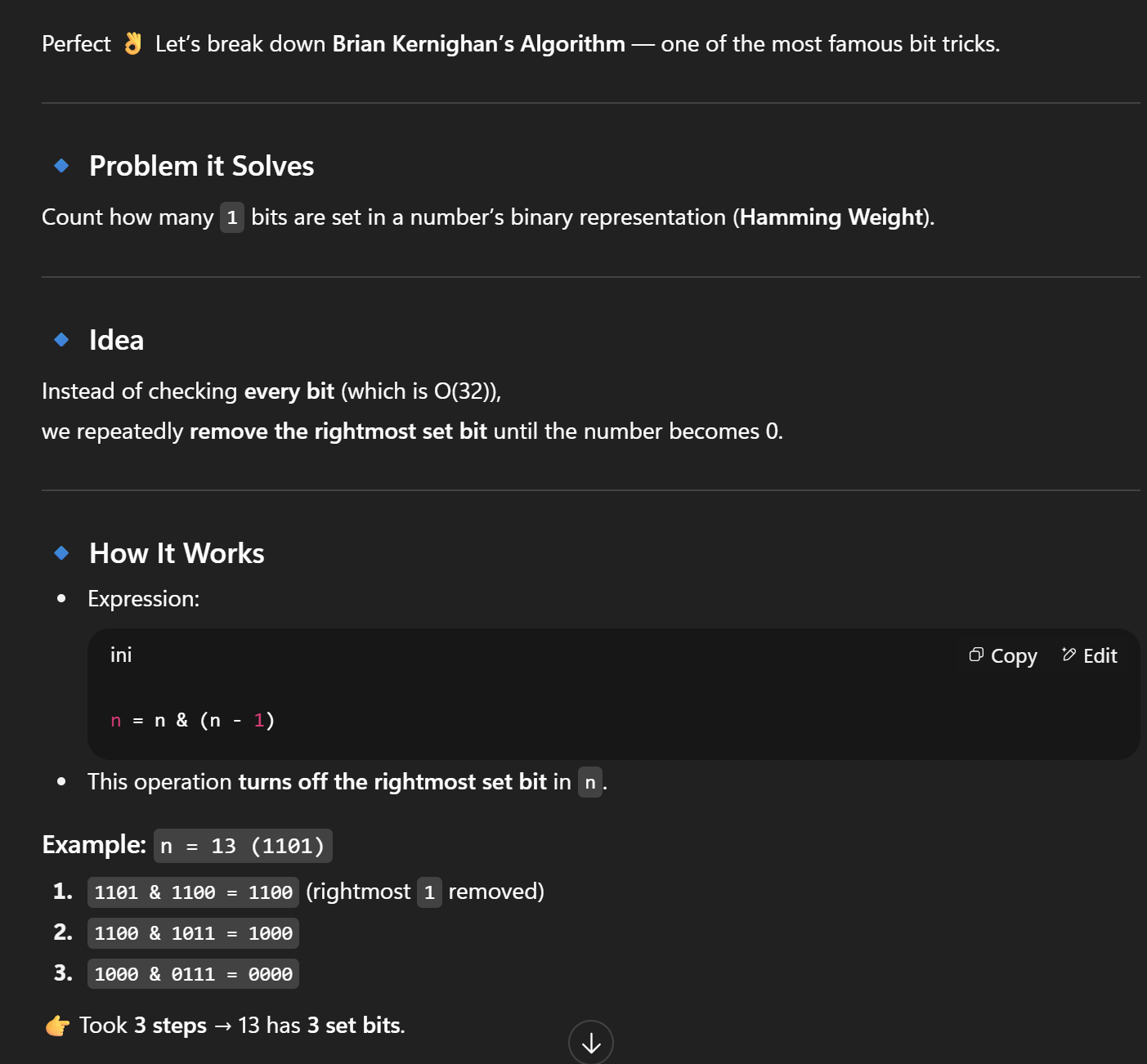
- Count set bits (Brian Kernighan’s Algo)
function countBits(n) {
let count = 0;
while (n > 0) {
n = n & (n - 1); // clears the lowest set bit
count++;
}
return count;
}
console.log(countBits(29)); // 4 (11101 has 4 set bits)
🔹 Common Use Cases
-
Checking even/odd quickly
-
Efficient multiplication/division by powers of 2
-
Bit masking (checking flags/permissions)
-
Swapping numbers without temp variable
-
Subset generation problems
-
Low-level optimizations in algorithms