Graph
Quick Tips
-
Please understand what kind of visited you need.
- Is it a visited set for backtracking? Delete current cell from visited once done with it. Why? https://neetcode.io/problems/matrixDFS
- When we’re searching for all possible paths (backtracking problems, e.g. word search, unique paths, flood-fill with multiple routes)
- We add the cell to
visitedto prevent cycles during the current DFS path. - Once we’ve finished exploring from that cell, we remove it (
visited.remove((r, c))) so that other paths can reuse the same cell. - Without removing, future DFS calls starting from different branches wouldn’t be able to visit this cell, even though logically it’s valid for a different path.
- If it just to avoid going there back - u dont need to delete it. https://neetcode.io/problems/matrixBFS
- Is it a visited set for backtracking? Delete current cell from visited once done with it. Why? https://neetcode.io/problems/matrixDFS
-
In BFS/DFS - when handling queue/stack and visited together: try to update both together. e.g. https://neetcode.io/problems/matrixBFS
- that prevents adding any cell again in queue.
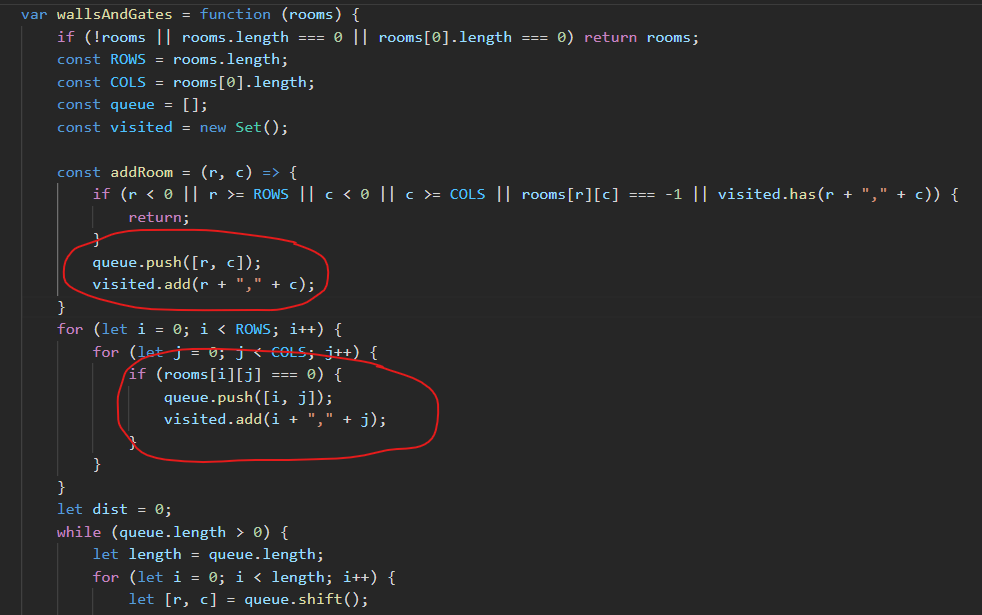
- that prevents adding any cell again in queue.
Warm up
- Structy - https://structy.net/problems/graph-intro
- Basic problems
- Traversal
- Path finding
- Cycle detection
- Basic mantra
- graph = nodes + edges
- Directed vs undirected
- Neighbors and Adjacency list
Visited Set - when to insert
Try to insert into visited when also inserting into queue (or something similar) so that you always act on "valid" things.
e.g. - Shortest Path code
const shortestPath = (edges, nodeA, nodeB) => {
const graph = buildGraph(edges);
const visited = new Set([ nodeA ]);
const queue = [[ nodeA, 0 ]];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const [ node, distance ] = queue.shift();
if (node === nodeB) return distance;
for (let neighbor of graph[node]) {
if (!visited.has(neighbor)) {
visited.add(neighbor);
queue.push([ neighbor, distance + 1 ]);
}
}
}
return -1;
};
const buildGraph = (edges) => {
const graph = {};
for (let edge of edges) {
const [a, b] = edge;
if (!(a in graph)) graph[a] = [];
if (!(b in graph)) graph[b] = [];
graph[a].push(b);
graph[b].push(a);
}
return graph;
};
Grid Graph Probs
- iterative + DFS Code with visited set
Island Count
const islandCount = (grid) => {
const ROWS = grid.length;
const COLS = grid[0].length;
let islands = 0;
let visited = new Set();
let getKey = (r, c) => r + "," + c;
const explore = (r, c) => {
if(r <0 || r >= ROWS) return false;
if(c <0 || c >= COLS) return false;
if(visited.has(getKey(r,c))) return false;
if(grid[r][c] === 'W') return false;
visited.add(getKey(r,c));
explore(r -1, c);
explore(r+1, c);
explore(r, c-1);
explore(r, c+1);
return true;
}
for(let r=0; r < ROWS; r++){
for(let c=0; c < COLS; c++){
if(explore(r ,c)) islands++;
}
}
return islands;
};
module.exports = {
islandCount,
};
Min Island
const minimumIsland = (grid) => {
let minIsland = Infinity;
const ROWS = grid.length;
const COLS = grid[0].length;
let visited = new Set();
let getKey = (r, c) => r + "," + c;
const explore = (r, c) => {
if(r <0 || r >= ROWS) return 0;
if(c <0 || c >= COLS) return 0;
if(visited.has(getKey(r,c))) return 0;
if(grid[r][c] === 'W') return 0;
visited.add(getKey(r,c));
return 1 + explore(r -1, c) + explore(r+1, c) + explore(r, c-1) + explore(r, c+1);
}
for(let r=0; r < ROWS; r++){
for(let c=0; c < COLS; c++){
const thisIsland = explore(r ,c);
if(thisIsland > 0)
minIsland = Math.min(thisIsland, minIsland);
}
}
return minIsland;
};
module.exports = {
minimumIsland,
};
White-grey-black cycle detection algo
(visited vs visiting)
only for DAG
white - unexplored
grey - visiting
black - already visited prev
Others
- js object keys are string - take care of them while making adjacency list object.