Getting Started - Microservices Architecture
Course link - https://courses.dometrain.com/courses/take/getting-started-microservices-architecture
Author - James
Monoliths
- Single codebase
- Deployed together
- Single process
- Monoliths starts slowing you down while scaling fast.
- deploying everything together might be problem for all modules
- size of teams!
- Monoliths !== legacy
- Well designed are still fantastic way to design modern applications
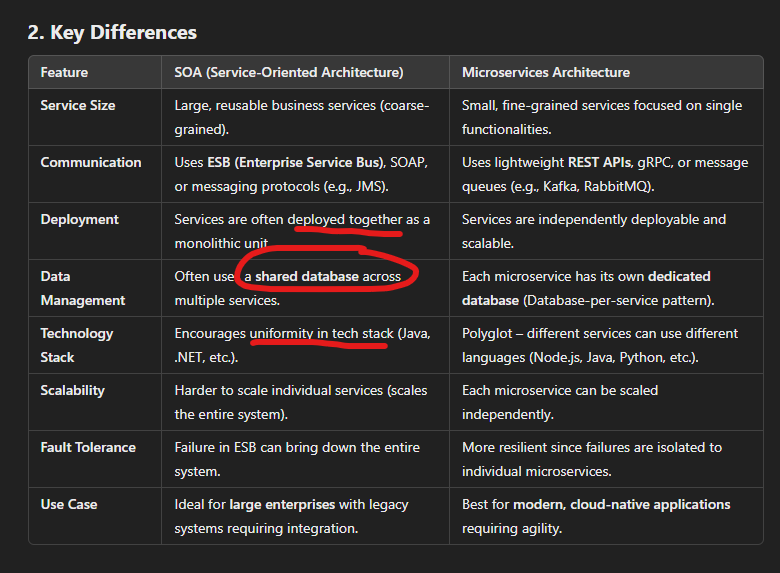
SOA
- first step of decomposing monoliths
- A service is aligned to an entire business domain.
- Certainly decomposed than monoliths, but not as granular as microservice.
- Payment, Order service etc.
SOA vs Microservice
Microservice
Microservices is an architectural style where an application is built as a collection of small, independent services, each focused on a single business capability and communicating via lightweight protocols (such as REST, gRPC, or message queues).
Microservices break applications into small, independent services that communicate via APIs, unlike monoliths that are tightly coupled.
- Single Responsibility – Each service does one thing well.
- Loose Coupling – Services communicate but are independent.
- Scalability – Can scale services individually.
- Resilience – Failure in one service doesn't bring down the whole system.
- Automation & CI/CD – Supports DevOps practices.
If asked about microservices, include these key aspects:
-
Decentralization: Each service has its own database and operates independently.
-
Autonomy: Services can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
-
Communication: Services interact via RESTful APIs, gRPC, or message brokers like Kafka, RabbitMQ.
-
Resilience: Failure of one service does not bring down the entire system.
-
Scalability: Each microservice can be scaled individually based on demand.
-
Technology Agnostic: Each service can be built using different technologies (polyglot architecture).
-
CI/CD & DevOps Friendly: Works well with containerization (Docker, Kubernetes) and automated deployments.
-
How do microservices communicate?
- Answer:
- Synchronous: REST APIs, gRPC
- Asynchronous: Message brokers (Kafka, RabbitMQ)
- Answer:
-
How do you handle data in microservices?
- Answer:
- Database per Service – Each service has its own DB.
- Event Sourcing – Track state changes as events.
- CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) – Separate read and write models.
- Answer:
-
How do you ensure security in microservices?
- Answer:
- Authentication: OAuth2, JWT, API Gateway
- Authorization: Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Service-to-Service Security: mTLS (Mutual TLS)
- Answer:
-
What are some challenges in microservices?
- Answer:
- Service Discovery: Need tools like Consul, Eureka.
- Data Consistency: Hard to maintain ACID transactions.
- Monitoring: Requires logging & tracing (ELK, Prometheus).
- Distributed Tracing: OpenTelemetry, Jaeger.
- Answer:
-
What tools are commonly used in microservices?
- Answer:
- API Gateway: Nginx, Kong, Apigee
- Service Discovery: Consul, Netflix Eureka
- Container Orchestration: Kubernetes, Docker
- Logging & Monitoring: ELK Stack, Prometheus, Grafana
- Answer:
Microservices are great when done correctly. However, there are bad of microservices:
- Many times people end up writing or designing a distributed monolithic.
- A tightly coupled system where no one can do anything unless without interacting others.
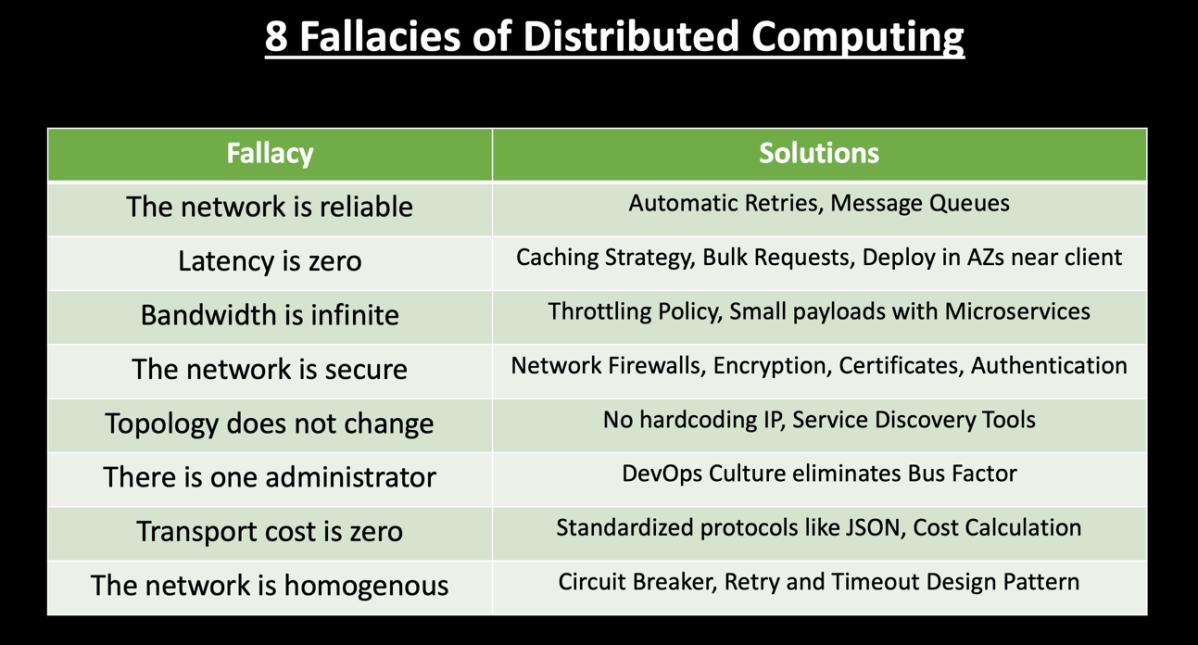
Eight fallacies of Distributed system:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fallacies_of_distributed_computing

Why DDD and Event storming?
- They help to determine microservice boundaries - the blue book by Eric
- Ubiquitous language - Agreed language across the whole team
- boundary context

- Event storming

Service Boundary
Boundaries should be aligned with a business domain.

Coupling and cohesion
Target "loose coupling, high cohesion" for stable system.
- Run time coupling
- Temporal coupling
- Content/data coupling
- functional coupling
- Sequential coupling
Cohesion - Things that change together - live together.
Cohesion is much simpler to get right than coupling.
Coupling is the silent killer in your application
- High coupling leads to 'distributed monolith'



Sharing data
