JWT and web security



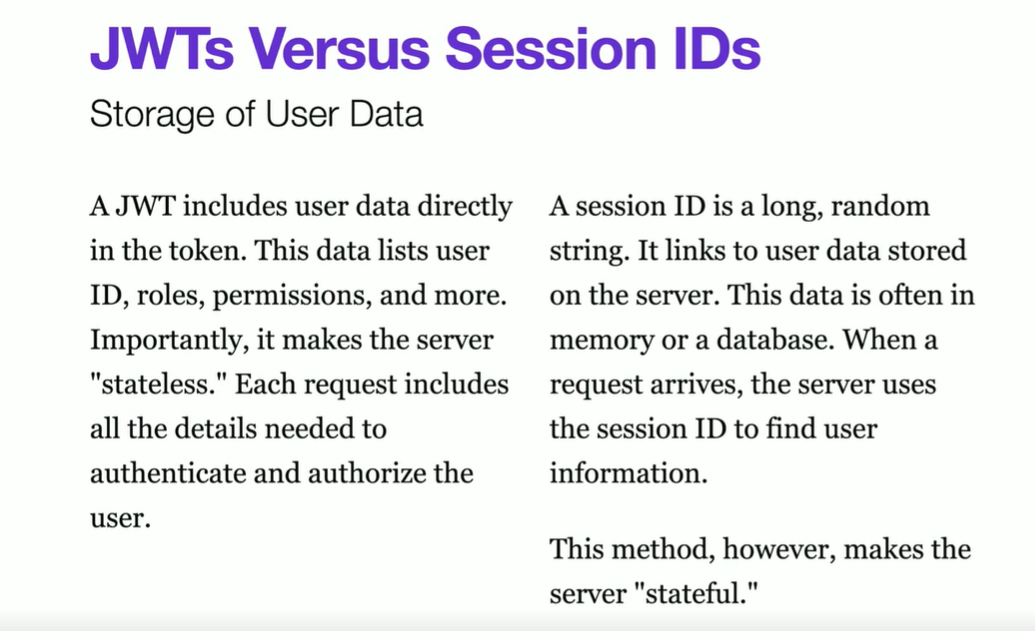
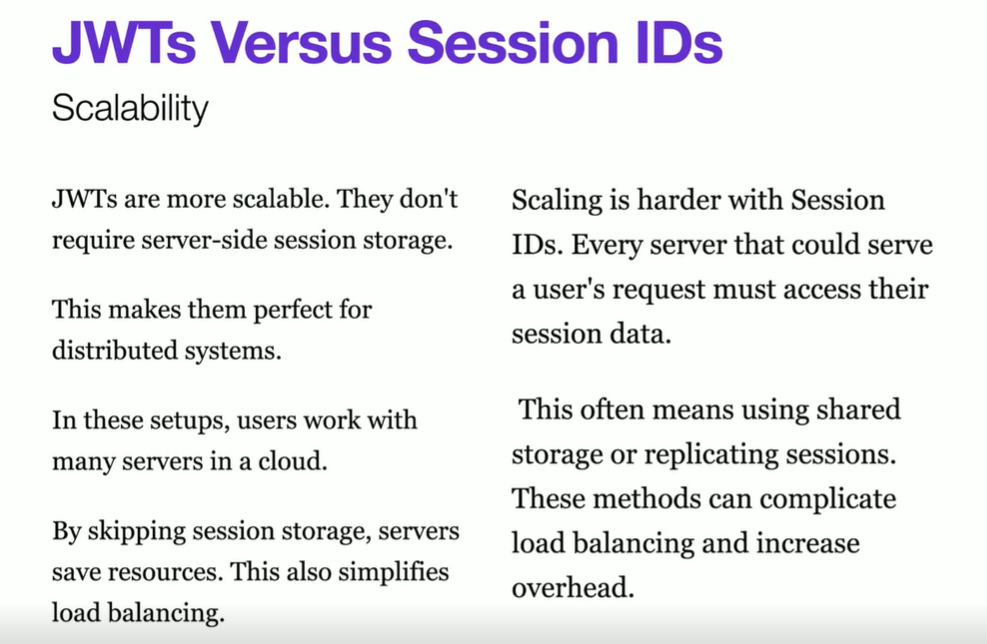









When saving JWT tokens, the best storage method depends on your security requirements and the type of token (access vs. refresh):
Best Practices for Storing JWT Tokens
1. Access Tokens (Short-lived)
-
Best Option: Memory (React State, Redux, etc.)
- Store the token in memory (e.g., React state, Redux, or a variable).
- Prevents Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
- Downside: The token is lost on page refresh.
-
Alternative: HttpOnly Cookies
- More secure but requires backend support.
- Automatically included in requests to the same domain.
- Prevents XSS attacks but vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF).
2. Refresh Tokens (Long-lived)
-
Best Option: HttpOnly Secure Cookies
- Cannot be accessed via JavaScript, preventing XSS.
- Must be refreshed via an endpoint that checks the token.
- Use
SameSite=Strictto mitigate CSRF attacks.
-
Avoid: Local Storage & Session Storage
- Vulnerable to XSS attacks. If an attacker injects JavaScript, they can steal the token.
Recommended Approach
- Store access tokens in memory.
- Store refresh tokens in HttpOnly Secure Cookies.
- Use the refresh token to obtain a new access token when needed.
Would you like guidance on implementing this in your React or Node.js app?
When using MSAL for React (@azure/msal-react), JWT tokens (ID token, access token, and refresh token equivalents) are stored based on the configured cache location in MSAL Configuration. The storage options are:
Where MSAL Saves JWT Tokens?
MSAL uses cacheLocation in its configuration to determine where it stores tokens:
- Local Storage (
localStorage) - Session Storage (
sessionStorage) - Memory (
"sessionStorage"by default)
Default Behavior
By default, MSAL stores tokens in sessionStorage, meaning:
- The tokens are cleared when the user closes the browser.
- The tokens are available only within the same session.
How to Configure Storage in MSAL?
You can specify where to store tokens in the cache configuration:
import { PublicClientApplication } from "@azure/msal-browser";
const msalConfig = {
auth: {
clientId: "YOUR_CLIENT_ID",
authority: "https://login.microsoftonline.com/YOUR_TENANT_ID",
redirectUri: "/",
},
cache: {
cacheLocation: "localStorage", // or "sessionStorage"
storeAuthStateInCookie: true, // Helps in certain browsers (IE11, Safari)
}
};
const msalInstance = new PublicClientApplication(msalConfig);
Storage Options & Security Considerations
| Storage Type | Persistence | Security | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| sessionStorage (default) | Cleared on browser close | Less risk of XSS attacks | Recommended for security |
| localStorage | Persists after browser close | Vulnerable to XSS | Use only if session persistence is required |
| Memory (Custom implementation) | Cleared on page refresh | Most secure, prevents XSS | Requires custom handling |
How to Clear Tokens?
To remove the tokens:
msalInstance.logoutRedirect(); // Logs out & clears tokens
msalInstance.logoutPopup(); // Logs out using a popup
Would you like help handling token expiration or silent authentication in your React app?