Client Server Communication
Non-IP based protocols
- Bluetooth
- Bluetooth is a technology that transmits data using radio waves between devices in close proximity.
- 2.4 GHz to 2.485 GHz frequency band
- slow data transfer rate of 1 - 3 Mbps.
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bluetooth/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bluetooth
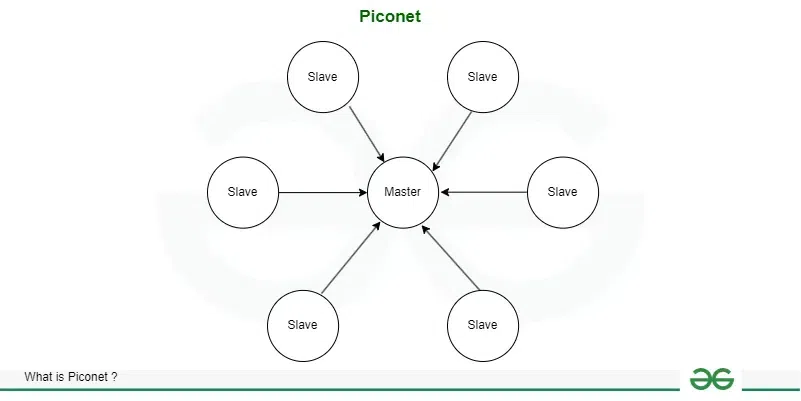
- Piconet is a type of Bluetooth network that contains one primary node called the master node and seven active secondary nodes called slave nodes. Thus, we can say that there is a total of 8 active nodes which are present at a distance of 10 meters.
- Piconet
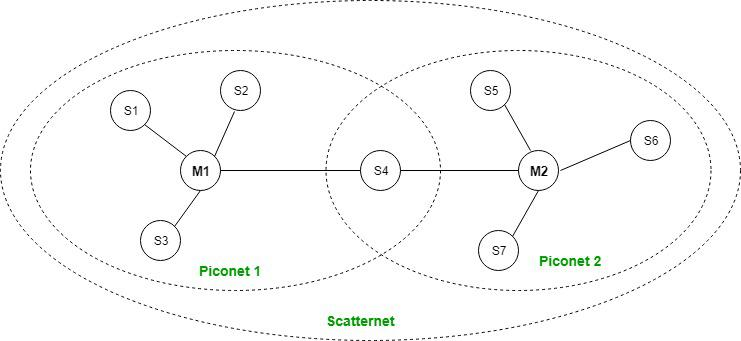
- Scatternet
- NFC (Near Field Communication)
- peer to peer communication mechanism that is unrelated to Internet Protocol
- It's very lightweight from the user's perspective and useful for transmitting small to medium sided units of data between peer devices
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HfMX_InfiP0
- NFC is a subset of RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and operates at 13.56 MHz.
- How it works
- Embedded NFC Chip – The card has an NFC chip that securely transmits payment data.
- RFID Technology – NFC is a subset of RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and operates at 13.56 MHz.
- Secure Transactions – The payment is encrypted and typically requires no PIN for small amounts.
- You can also use NFC via mobile wallets like Google Pay, Apple Pay, or Samsung Pay, which store your credit card details and use the phone's NFC chip for payments.
- Older cards had EMV - An EMV chip (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) is a smart chip embedded in credit and debit cards that enhances security by storing and encrypting payment data
NFC vs. Bluetooth: Which is Faster?
NFC is generally slower than Bluetooth, but it is optimized for quick, short-range transactions rather than high-speed data transfer.
Speed Comparison
- NFC: Maximum speed of 424 kbps (kilobits per second)
- Bluetooth (Classic): Up to 3 Mbps (megabits per second)
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): Up to 2 Mbps
Why NFC is Slower but Still Useful
- Instant Connection: NFC connects in less than 0.1 seconds, whereas Bluetooth requires pairing.
- Low Power Consumption: NFC uses very little energy, making it ideal for contactless payments and tap-to-share applications.
- Security: Since NFC operates at very short ranges (~4 cm), it's more secure for financial transactions.
When to Use What?
- NFC: Best for contactless payments, keyless entry, and quick data exchanges (e.g., tap-to-share).
- Bluetooth: Best for audio streaming, file transfers, and continuous data exchange (e.g., wireless headphones, smartwatches).