Cassandra
https://www.scylladb.com/glossary/wide-column-database/
Most important thing - Primary Key
- Cassandra was originally built by Facebook to support its rapidly scaling inbox search feature.
- implements a partitioned wide-column storage model with eventually consistent semantics.
- It is a distributed database that runs in a cluster and can horizontally scale via commodity hardware.
Data model
Keyspace = Database
Table = Table
Row = Row : Container of data. Represented by a primary key and contains columns.
Column:
- A column is represented by a name, a type, and a value corresponding to the value of that column for a row
- every column has timestamp metadata associated with it, denoting when it was written. When a column has a write conflict between replicas, it is resolved via "last write wins".
- Cassandra columns support a plethora of types, including user-defined types and JSON values. This makes Cassandra very flexible as a data store for both flat and nested data
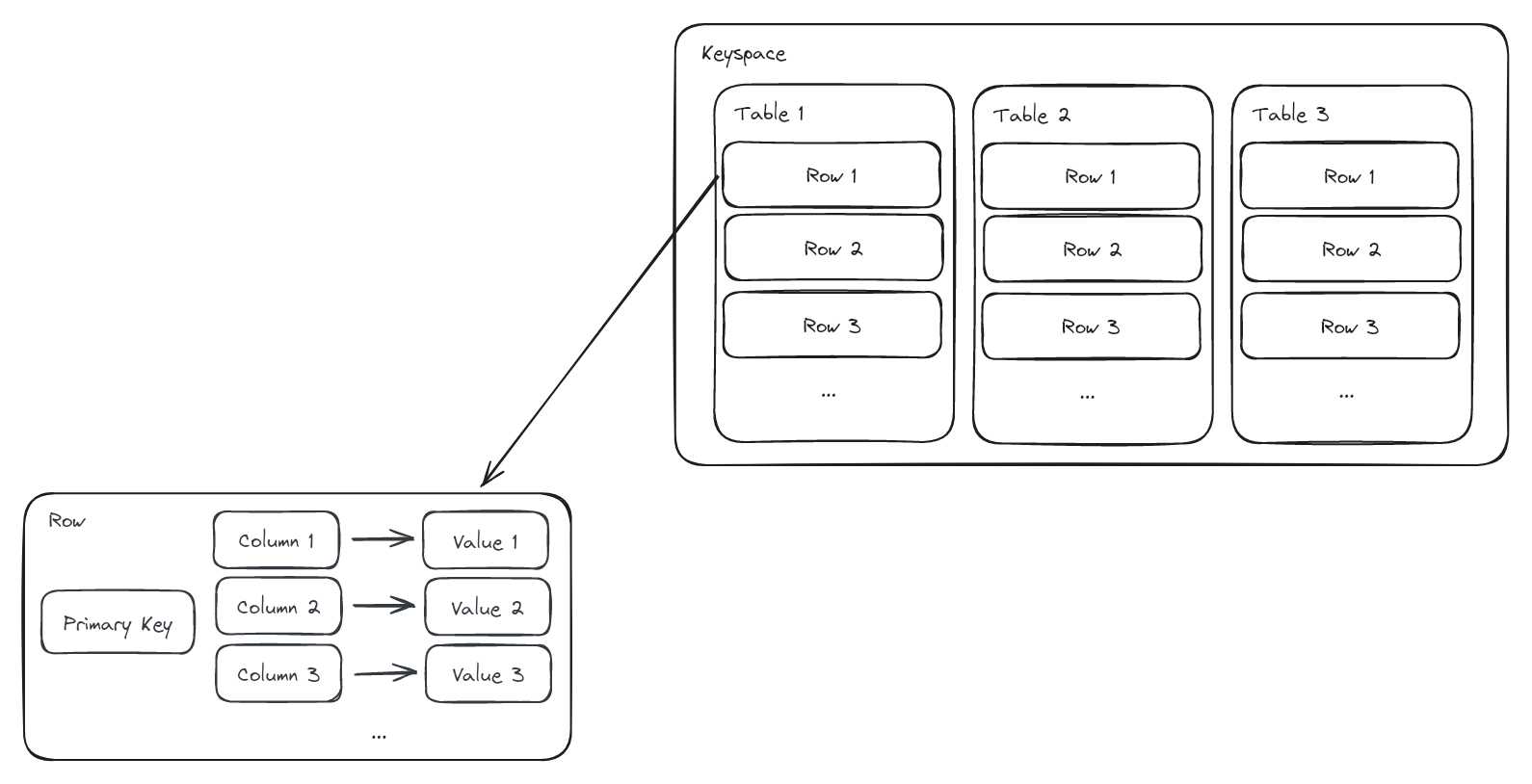
Primary Key
One of the most important constructs in Cassandra is the "primary key" of a table. Every row is represented uniquely by a primary key.
A primary key consists of one or more partition keys and may include clustering keys.
-
Partition Key - One or more columns that are used to determine what partition the row is in.
-
Clustering / Sorting Key - Zero or more columns that are used to determine the sorted order of rows in a table. Data ordering is important depending on one's data modeling needs, so Cassandra gives users control over this via the clustering keys.
-- Primary key with partition key a, no clustering keys
CREATE TABLE t (a text, b text, c text, PRIMARY KEY (a));
-- Primary key with partition key a, clustering key b ascending
CREATE TABLE t (a text, b text, c text PRIMARY KEY ((a), b))
WITH CLUSTERING ORDER BY (b ASC);
-- Primary key with composite partition key a + b, clustering key c
CREATE TABLE t (a text, b text, c text, d text, PRIMARY KEY ((a, b), c));
-- Primary key with partition key a, clustering keys b + c
CREATE TABLE t (a text, b text, c text, d text, PRIMARY KEY ((a), b, c));
-- Primary key with partition key a, clustering keys b + c (alternative syntax)
CREATE TABLE t (a text, b text, c text, d text, PRIMARY KEY (a, b, c));
Partitioning
- Cassandra achieves horizontal scalability by partitioning data across many nodes in its cluster.
- In order to partition data successfully, Cassandra makes use of consistent hashing with virtual nodes.
- Consistent hashing is a fundamental technique used in distributed systems to partition data / load across machines in a way that prioritizes evenness of distribution while minimizing re-mapping of data if a node enters or leaves the system.
Replication
In Cassandra, partitions of data are replicated to nodes on the ring, enabling it to skew extremely available for system designs that rely on that feature. Keyspaces have replication configurations specified and this affects the way Cassandra replicates data.
At a high level, Cassandra chooses what nodes to replicate data to by scanning clockwise from the vnode that corresponds to hashed value in a consistent hashing scheme. For example, if Cassandra is trying to replicate data to 3 nodes, it will hash a value to a node and scan clockwise to find 2 additional vnodes to serve as replicas. Of note, Cassandra skips any vnodes that are on the same physical node as vnodes already in the replica set so that several replicas aren't down when a single physical node goes down.
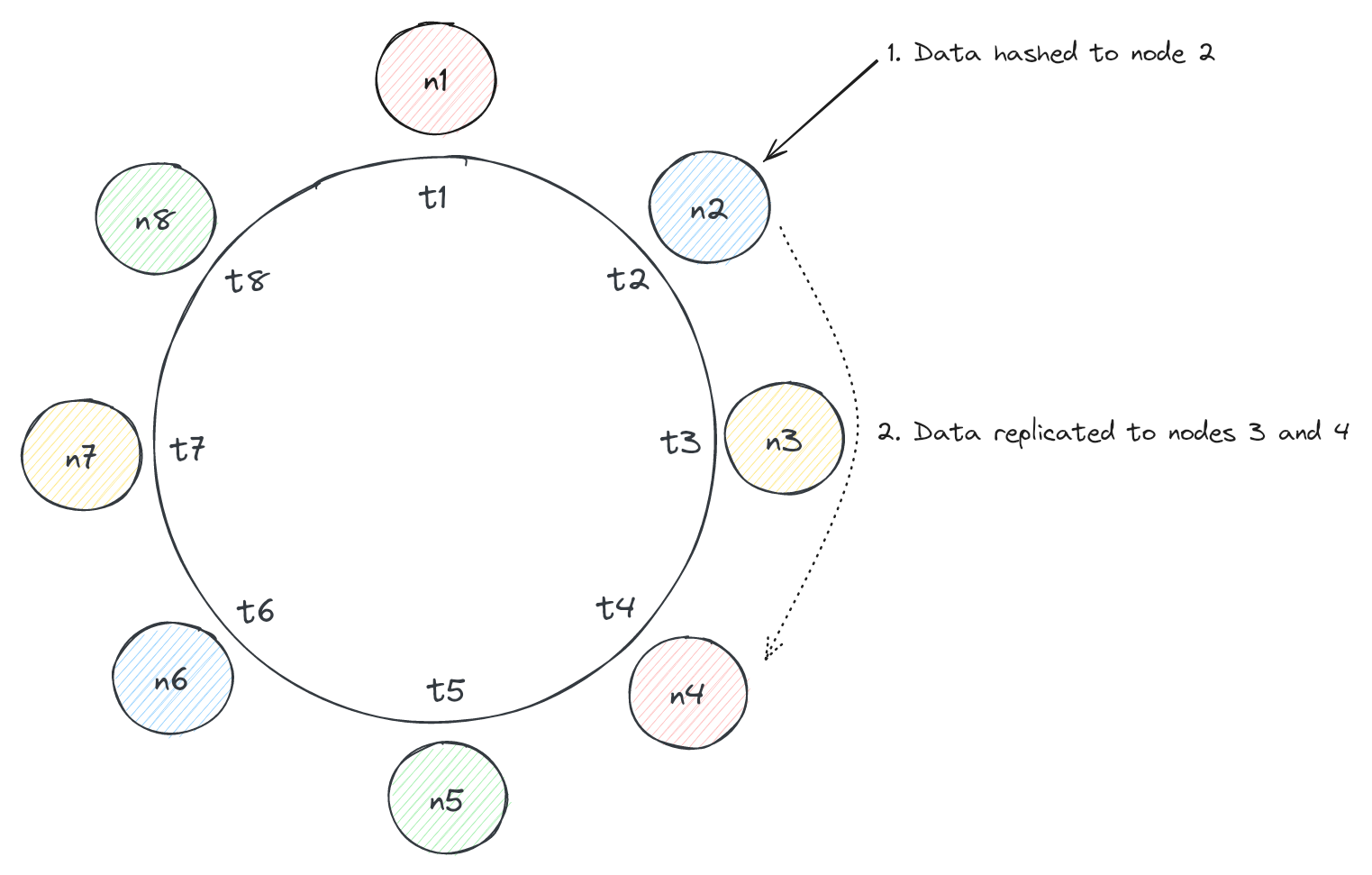
Replication Strategy
Cassandra has two different replication strategies
NetworkTopologyStrategy is the strategy recommended for production and is data center / rack aware so that data replicas are stored across potentially many data centers in case of an outage. It also allows for replicas to be stored on distinct racks in case a rack in a data center goes down. The main goal with this configuration is to establish enough physical separate of replicas to avoid many replicas being affected by a real world outage / incident.
SimpleStrategy is a simpler strategy, merely determining replicas via scanning clockwise (this is the one we discussed above). It is useful for simple deployments and testing.
Below is Cassandra CQL for specifying different replication strategy configurations for a keyspace:
-- 3 replicas
ALTER KEYSPACE hello_interview WITH REPLICATION = { 'class' : 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 3 };
-- 3 replicas in data center 1, 2 replicas in data center 2
ALTER KEYSPACE hello_interview WITH REPLICATION = {'class' : 'NetworkTopologyStrategy', 'dc1' : 3, 'dc2' : 2};