_index
Core Database
Almost all system design problems will require you to store some data and you're most likely going to be storing it in a database (or Blob Storage). While there are many different types of databases, the most common are relational databases (e.g. Postgres) and NoSQL databases (e.g. DynamoDB) - we recommend you pick one of these for your interview. If you are taking predominantly product design interviews, we recommend you pick a relational database. If you are taking predominantly infrastructure design interviews, we recommend you pick a NoSQL database.
Many candidates trip themselves up by trying to insert a comparison of relational and NoSQL databases into their answer. The reality is that these two technologies are highly overlapping and broad statements like "I need to use a relational database because I have relationships in my data" (NoSQL databases can work great for this) or "I've gotta use NoSQL because I need scale and performance" (relational databases, used correctly, perform and scale incredibly well) are often yellow flags that reveal inexperience.
Here's the truth: most interviewers don't need an explicit comparison of SQL and NoSQL databases in your session and it's a pothole you should completely avoid. Instead, talk about what you know about the database you're using and how it will help you solve the problem at hand. If you're asked to compare, focus on the differences in the databases you're familiar with and how they would impact your design. So "I'm using Postgres here because its ACID properties will allow me to maintain data integrity" is a great leader.
Deep dive on how database works - https://cstack.github.io/db_tutorial/
NoSQL Databases
What is a NoSQL database and when should you use it?
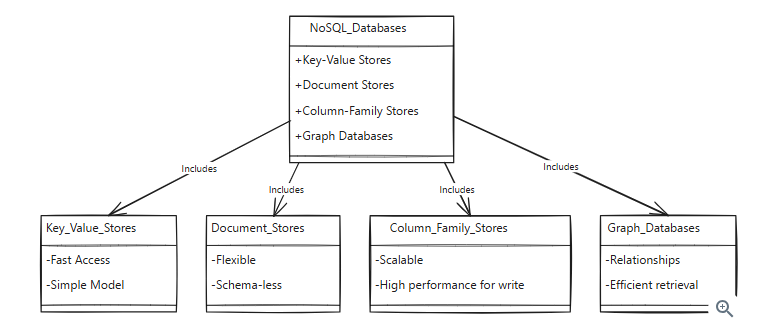
NoSQL databases are a broad category of databases designed to accommodate a wide range of data models, including key-value, document, column-family, and graph formats. Unlike relational databases, NoSQL databases do not use a traditional table-based structure and are often schema-less. This flexibility allows NoSQL databases to handle large volumes of unstructured, semi-structured, or structured data, and to scale horizontally with ease.
The places where NoSQL databases excel are not necessarily places where relational databases fail (and vice-versa). For example, while NoSQL databases are great for handling unstructured data, relational databases can also have JSON columns with flexible schemas. While NoSQL databases are great for scaling horizontally, relational databases can also scale horizontally with the right architecture. When you're discussing NoSQL databases in your system design interview, make sure you're not making broad statements but instead discussing the specific features of the database you're using and how they will help you solve the problem at hand.
Things you should know about NoSQL databases
-
Data Models: NoSQL databases come in many different flavors, each with its own data model. The most common types of NoSQL databases are key-value stores, document stores, column-family stores, and graph databases.
-
Consistency Models: NoSQL databases offer various consistency models ranging from strong to eventual consistency. Strong consistency ensures that all nodes in the system have the same data at the same time, while eventual consistency ensures that all nodes will eventually have the same data.
-
Indexing: Just like with relational databases, NoSQL databases support indexing to make data faster to query. The most common types of indexes are B-Tree and Hash Table indexes.
-
Scalability: NoSQL databases scale horizontally by using consistent hashing and/or sharding to distribute data across many servers.